From Virtual Reality to eXtended Reality
Technologies, characteristics, expectations, uses… in comparison
In the era of Digital Transformation, eXtended Reality encompasses some of the most promising enabling technologies with the potential to reconfigure business processes, but some aspects are still not clear and above all it is difficult to orient yourself among Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR), and Extended Reality (XR).
These categories are constantly evolving as quickly as the technologies offer new opportunities of development. For this reason, the borderlines of those categories are fluid and often reflect the background (e.g. academics, marketers etc.) of those who define them, for instance users often use Virtual Reality to refer to any application related to a virtual environment.
With the help of our professional partners, we try to address this topic by trying to clarify the distinction with some examples.
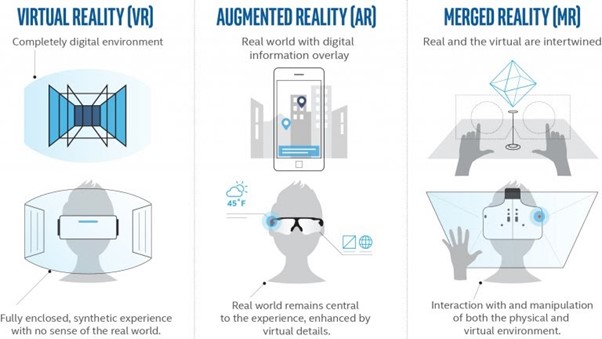
Virtual, augmented and merged/mixed reality in comparison. Source: extremetech.com
Virtual Reality (VR)
VR is an immersive experience that consists of isolating ourselves from the real and surrounding environment thanks to the use of wearable devices (such as visors, and headsets). VR allows users to completely immerse themselves in an entirely virtual world, which replicates a real environment or an imaginary world, and where users can interact with elements as if they were actually inside it.

Here are some examples of VR applications in some of the world’s most important museums such as Louvre or London’s Tate Modern
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR enriches our existing reality by overlaying digital content on it. The real world elements are enriched (actually augmented) by computer-generated input such as sound, video, graphics or GPS data.
AR experiences are obtained thanks to the camera of common mobile and tablets, but also thanks to special viewers such as smart glasses which project digital elements onto the field of vision, without the possibility to physically interact.

Examples: If you haven’t played it, you will certainly have heard of Nintendo’s Pokémon Go App, which was an overwhelming success, with up to 65 million users at the peak of its popularity.
If you want to decorate your home from the comfort of your sofa at home, you can use the IKEA Place app, which now allows you to select anything from the store’s catalog and see how it will look to scale anywhere in your house (as you may remember Edward Norton doing in the film Fight Club).
Mixed (or Merged) Reality (MR)
Mixed reality relies on all the technologies used by AR, but provides to the device the environment understanding which makes it possible to have a tight and natural integration of the real and augmented worlds.
The devices that are able to do Mixed Reality have:
- an advanced CPU/GPU processors which is able to do SLAM algorithms (Simultaneous localization and mapping) in order to understand the environment and the user position,
- (optional) depth sensors to further understand the depth of the environment such as people and hand gestures
- (optional) a lidar 3d scanning sensor which scans the actual environment for greater accuracy.
In this way, devices are able to place virtual objects in a real surrounding and have the user walk through it, understanding not only his position but many other features like floors, walls etc.
The goal of mixed reality is to add digital information about the physical world in real time, and allow the user to physically interact with them.
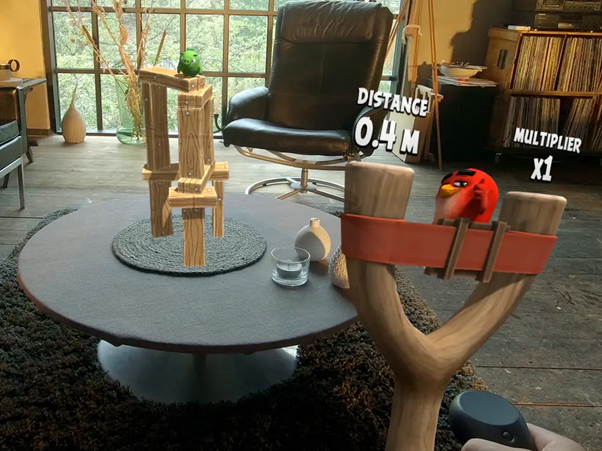

Credits: https://www.rovio.com
Examples: Angry Birds game is one of the examples of MR. In fact, because of the combination between physical and digital world, MR has opened the door to a brand new era in gaming by introducing the real world into an immersive gaming experience.
Other examples of Mixed Reality in Business, Gaming, and E-learning: https://postindustria.com/mixed-reality-examples-in-business-gaming-and-e-learning/
eXtended Reality (XR)
Within the immersive technologies scenario, XR represents the fusion of VR and MR extended by other senses, like haptic of objects or walls, heat, smell or free roaming in large-scale locations, often combined with multi-user capability.
Bounded with several of these interfaces XR provides the most immersive experience for the user. Due to additional hardware most applications are installed in specialized premises. XR is mainly used for location-based-entertainment (LBE) and for educational or training applications.

Train engineer. Source: https://vrtech.global/industrial_solutions#training-vr
Educational and training segment examples are still rare, here some examples for industrial training:
Most examples come from the entertainment sector. Here you can see how to hunt Zombie shooter with vibrating guns:
Last but not least, Bridges is an example of XR!
We are developing advanced training scenarios for firefighters simulations and as educational resources for informal learning:


